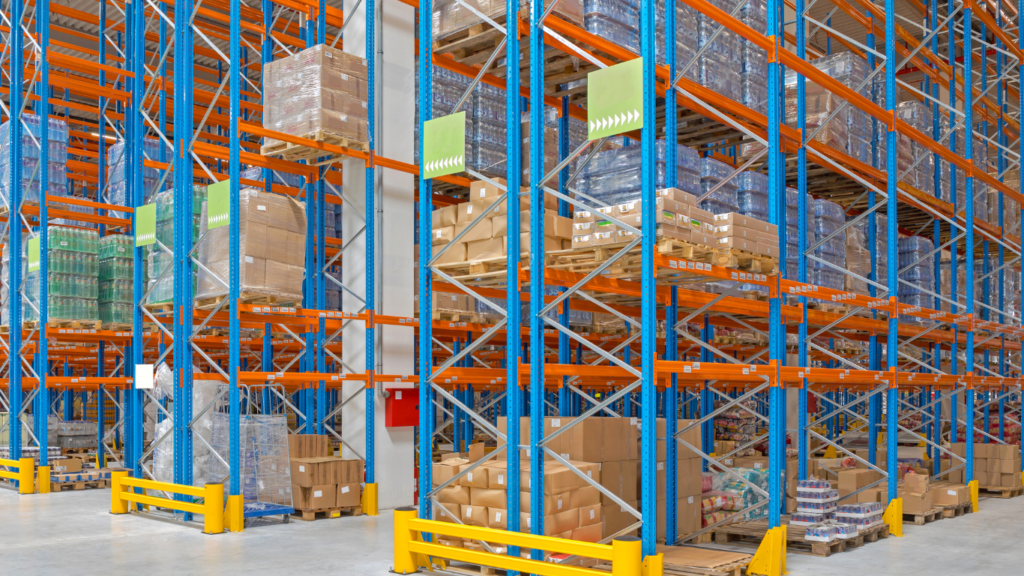
Efficient warehouse management is crucial for businesses looking to streamline their operations and maximize productivity. One key aspect of warehouse management is configuring unit load types within a Warehouse Management System (WMS). In this blog post, we will explore the importance of unit load types and guide you through the process of configuring them in your WMS, helping you enhance your warehouse efficiency.
What is unit load?
In warehouse management system, “unit load types” refer to the different forms or configurations in which goods or products are grouped together for storage, handling, and transportation within a warehouse or distribution center. Unit load types are designed to facilitate efficient movement and storage of goods, optimize space utilization, and enhance operational processes.
6 common load types in a warehouse
Here are 6 common unit load types used in warehouse management:
- Pallets: Pallets are wooden, plastic, or metal platforms used to stack goods. They are the most widely used unit load type in warehousing. Palletized loads can be easily moved using forklifts or pallet jacks, allowing for efficient storage and transportation.
- Containers: Containers are standardized, reusable units used for shipping and storing goods. They come in various sizes, such as intermodal containers for long-distance transport or roll cages for intra-warehouse movement.
- Skids: Skids are similar to pallets, but they lack a bottom deck. They are primarily used for handling heavy or oversized items, such as machinery or large appliances.
- Totes or Bins: Totes or bins are smaller, stackable containers used for storing and transporting small parts or components. They are commonly used in order picking and assembly processes.
- Drums: Drums are cylindrical containers typically used for storing liquids or granular materials. They are often stacked on pallets for ease of handling.
- Bulk: Bulk refers to loose materials or products that are not contained within specific unit load types. Bulk items, such as grains or powders, are typically stored in specialized containers like silos or bins.
Configuring unit load types in SwiftHub
Configuring unit load types in SwiftHub is a critical step towards optimizing warehouse efficiency. By defining unit load types, creating master data, configuring storage locations, handling equipment, and establishing rules and workflows, you can streamline your warehouse operations, enhance inventory management, and achieve higher productivity levels. With careful configuration and integration, SwiftHub is a powerful tool in driving warehouse efficiency and meeting customer demands.
To configure a unit load type in SwiftHub, start by defining its specific characteristics and attributes. Consider factors such as dimensions, weight capacity, stackability, and load-bearing capacity. By clearly defining these parameters, you ensure that the WMS can accurately handle and manage the unit load type.
Creating Unit Load Type Master Data
Once the unit load type characteristics are defined, it’s time to create a master data record in SwiftHub. This record will store all the relevant information about the unit load type, including its unique identifier, description, and associated parameters. Having centralized master data ensures consistency and ease of access across different warehouse processes.
Configuring Storage Locations
Identify suitable storage locations within your warehouse for the unit load type. Define specific areas, racks, or zones that can accommodate the unit load type based on factors like size, weight capacity, and accessibility. This step helps optimize storage space and ensures efficient retrieval of goods during picking and packing operations.
Configuring Handling Equipment
Specify the types of handling equipment required to efficiently manage the unit load type. Determine whether forklifts, pallet jacks, AGVs, or other equipment are needed. Configure the WMS to recognize the equipment’s capabilities, such as load capacity and compatibility with the unit load type. This integration ensures seamless material handling operations.
Establishing Handling Rules
Define handling rules for the unit load type, including stacking, de-stacking, picking, and transportation guidelines. Consider factors such as maximum stacking heights, stacking patterns, handling sequences, and safety considerations. By establishing clear rules, you ensure safe and efficient handling of the unit load type throughout your warehouse.
Testing and Validation
Before deploying the configured unit load types in a live environment, perform thorough testing and validation. Conduct test scenarios to ensure the system behaves as expected. Validate that the configuration aligns with your warehouse’s operational requirements and addresses any potential issues or limitations.
Conclusion
The choice of unit load type depends on factors such as the nature of the goods, their weight and dimensions, storage requirements, handling equipment available, and the specific processes within the warehouse. By standardizing unit load types, warehouses can streamline operations, improve inventory management, and ensure the safe and efficient movement of goods.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

