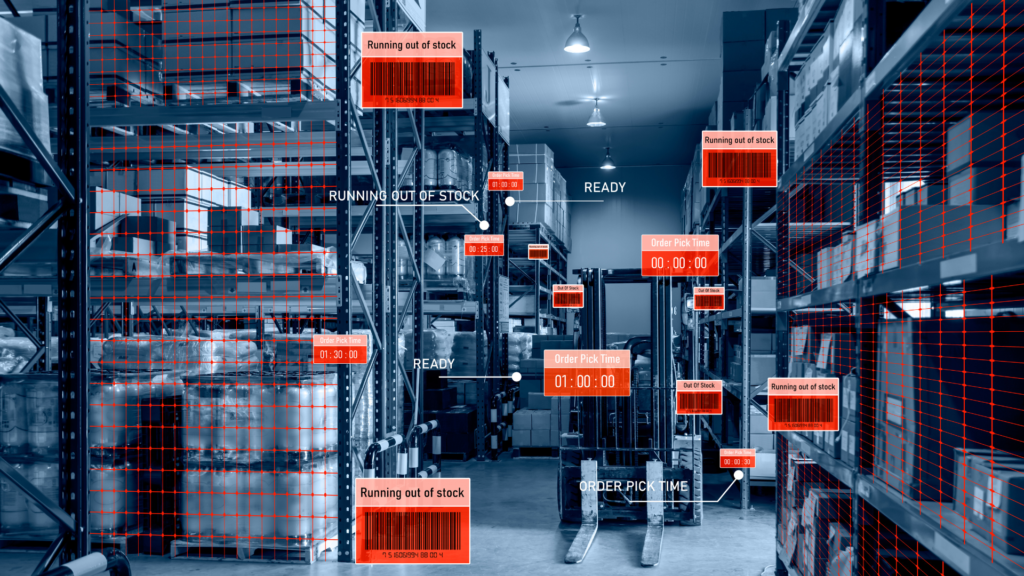
Efficient inventory management is crucial for businesses to optimize operations, minimize costs, and meet customer demands. In this blog post, we will explore different methods of inventory management that can help businesses streamline their processes and achieve maximum efficiency. From traditional methods like FIFO, FEFO, and LIFO to more advanced techniques like ABC analysis, Just-in-Time (JIT), Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Safety Stock, and Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI), each method offers unique advantages based on specific business needs and industry requirements. Understanding these methods will empower businesses to make informed decisions and enhance their overall inventory management practices.

- FIFO (First-In, First-Out): FIFO is a widely adopted method where the oldest inventory items are used or sold first. By prioritizing the consumption of older stock, businesses can reduce waste, prevent product expiration, and maintain product quality. FIFO is particularly useful in industries with perishable goods or products that have a limited shelf life.
- FEFO (First-Expired, First-Out): FEFO is a variation of FIFO that places emphasis on the expiration date of products. It ensures that products with the closest expiration dates are used or sold first, reducing the risk of selling expired goods. This method is crucial in industries where product safety and compliance are paramount, such as pharmaceuticals or food.
- LIFO (Last-In, First-Out): LIFO is the opposite of FIFO, where the most recently received inventory items are used or sold first. While less commonly used in warehouse management, LIFO can be beneficial in industries where inventory costs tend to rise over time, such as during inflationary periods. However, it may not accurately reflect the actual cost of inventory.
- ABC Analysis: ABC analysis categorizes inventory items based on their value and importance. Classifying items as A, B, or C helps businesses allocate resources effectively and prioritize inventory management efforts. Class A items are high-value and high-priority, while Class C items are low-value and low-priority. This method ensures that attention is focused on managing the most critical items.
- Just-in-Time (JIT): JIT is a method where inventory is ordered and received only when needed for production or customer orders. This approach minimizes carrying costs associated with holding excess inventory and emphasizes the importance of accurate demand forecasting and close collaboration with suppliers.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): EOQ is a formula-based method that calculates the optimal order quantity to minimize the total cost of inventory. By balancing ordering costs and carrying costs, businesses can determine the most cost-effective order quantity and frequency.
- Safety Stock: Safety stock is an additional inventory buffer maintained to mitigate unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply chain disruptions. It acts as a safety net, ensuring that customer orders can be fulfilled even during unforeseen circumstances.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): VMI is a collaborative approach where the supplier takes responsibility for monitoring and replenishing inventory levels at the customer’s location. By leveraging real-time data and close collaboration, VMI helps optimize inventory levels, reducing the customer’s burden of inventory management.
Effective inventory management is vital for businesses to optimize operations, minimize costs, and meet customer expectations. By understanding and implementing various inventory management methods such as FIFO, FEFO, LIFO, ABC analysis, JIT, EOQ, safety stock, and VMI, businesses can enhance their inventory control, reduce waste, improve product quality, and maintain optimal inventory levels. Choosing the right combination of methods based on industry requirements, product characteristics, and business objectives will result in streamlined operations, improved profitability, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Investing in a robust warehouse management system (WMS) can further empower businesses to leverage these methods efficiently
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

